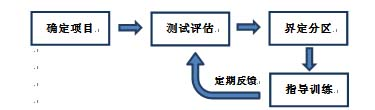
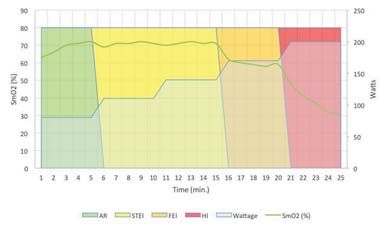
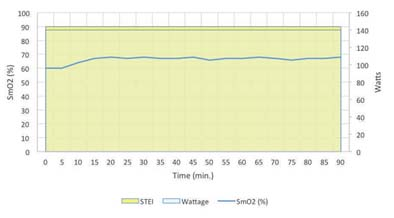
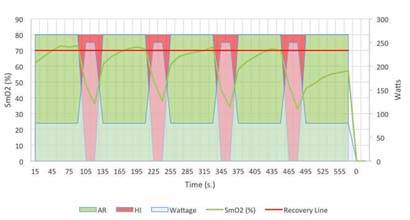
First, the introduction In the endurance training process, it is very important to understand how the human body produces energy, which ensures that the correct energy consumption pathway is activated and trained, thus appropriately improving the athlete's athletic ability. Muscle oxygen helps determine the transport and utilization of oxygen during the exchange process – these two parameters are decisive data in the energy production process. The basic trend of muscle oxygen can indicate changes in energy metabolism during the test. These trend data obtained through a simple test program can provide athletes with a basic endurance training interval. Then, the athlete/coach can perform training and implementation monitoring of the athletes based on these divisions. Please note!! These evaluation results have the specificity of the sports program. That is to say, the training interval obtained by the bicycle evaluation program can only be used for bicycle projects, but it cannot be accurately used for running or other sports. Second, the guiding process Use the muscle oxygen monitoring indicators to guide the endurance training flow chart 1, determine the project According to the training objectives, the trainee is determined to participate in the project. 2, test evaluation The purpose of the test is to determine the muscle oxygen function partition and load intensity of the trainee in the exercise program, and to develop a later training plan. Therefore, the test plan should be as consistent as possible with the actual training. This article takes the bicycle 5min incremental load test as an example. The equipment needed for the test included: a muscle oxygen monitor, a bicycle capable of monitoring power and strength, and a stopwatch. It is recommended to start the test at a low intensity level (without warming up), for example, starting at 80 watts and maintaining this intensity for 5 minutes. After 5 minutes, the strength was increased at a level of about 20-30 watts and held for 5 minutes. Then, continue to increase the intensity at a level of 20-30 watts per stage and maintain it for 5 minutes at each stage until Moxy shows a continuous decrease in muscle oxygen. When this continuous drastic decline occurs, the test can be stopped and the data can be used for analysis. 3. Define the partition Incremental Endurance Training Muscle Oxygen Zone Legend This test will provide the trainer with 3 or 4 training intensity intervals, which are determined by a number of different factors; 4 possible interval curves and illustrations can refer to the above figure (3 intervals are often structural) Endurance and functional endurance intervals were combined). These intervals were interpreted by the trend of muscle oxygen consumption in the 5-minute incremental load test. The incremental trend at the beginning can determine the intensity interval for positive recovery (AR), as indicated by the green interval (if your data does not have an increasing trend at the beginning, retest at a lower intensity). Muscle oxygen can determine the structural endurance (STEI) intensity interval at the plateau of the highest point, as indicated by the yellow interval. The second myocardium plateau, the lower myoelectric value platform, is not required. This value is the functional endurance (FEI) intensity interval, as shown in the orange interval. Clear and continuous decline in muscle oxygen values ​​can determine large intensity (HI) intervals, as indicated by the red areas. 4. Guided training 1) Long distance slow ride Long-distance slow training is the standard form of training for most endurance sports. This refers to maintaining the strength of the target throughout the long distance training session. The goal of long-distance slow training is to improve endurance; to properly improve endurance, the corresponding energy consumption path must be trained. In the interval measured, the strength within the structural endurance (STEI) intensity interval ensures maximum oxygen utilization during energy production – this is the goal of long-distance slow training. The muscle oxygen characteristic curve of long distance slow training is similar to the following figure. The time during the training is greater than 50 minutes and the intensity remains within the STEI interval. To control training at this intensity requires close attention to the athlete's muscle oxygen level, which is close to the maximum in the STEI interval of the test and is stable in this area. Long-distance slow training muscle oxygen characteristic curve 2) Interval training Interval training is a form of exercise that simultaneously increases athletes' endurance and strength. The training method shown in the figure below is for the low-intensity training of the active recovery interval intermittently during the period of high-intensity training. As shown in the figure, the trainee completed the intensity training of the 30-second high-intensity interval after performing the intensity training of the 90-second active recovery interval. Pay attention to the muscle oxygen value while repeating this mode repeatedly, especially when low-intensity training in the recovery phase requires attention to how muscle oxygen recovers. Based on the recovery baseline indicated by the red line, it is ensured that the muscle oxygen in the recovery phase can return to the baseline level. When muscle oxygen can no longer return to baseline, training should be over. Intermittent training muscle oxygen characteristic curve 3) Restorative training Restorative training is often used during regular training, which is to determine the importance of the positive recovery interval. In intensity training during the positivity recovery interval, the muscle oxygen value will increase to the maximum so that the oxygen supply exceeds the amount required for its consumption, which minimizes the activated muscle pressure. Moreover, during training, the heart and respiratory function are enhanced, and more blood is delivered to the muscles that consume a lot of oxygen at work. If the muscles work at a lower intensity, this training will speed up recovery. This form and intensity level of training also applies to relaxation exercises after the game and after strength training. 4) Preparation before the game During the offseason, the long-distance slow training is used to improve the athlete's structural endurance (STEI) level, so the athlete's functional endurance level should be improved before the game. This means that athletes must maximize their potential by improving the nervous system and the ability of enzymes to adapt quickly. In order to achieve this goal, it is first necessary to determine the time required for the athlete to play in the game (for example, if the game is 60 minutes, the athletes should be trained in 60 minutes of functional adaptation). In other words, it is necessary for the athlete to maintain the training intensity at the maximum of the functional endurance (FEI) intensity interval as much as possible in this corresponding training time or distance. 5, regular feedback After undergoing a training period of one stage, it is necessary to conduct another test evaluation according to the actual situation. On the one hand, it is an observation of the training effect, and also a guide for the next stage of training. Similar projects include long-distance running, marathon, triathlon, long-distance ice and snow, swimming and other endurance training. Makeup Brush-Mini Set,Beauty Brush,Foundation Makeup Brush,Powder Foundation Brush SZ CHENGYANG BEAUTY TOOLS CO.,LTD , https://www.cyfootfile.com