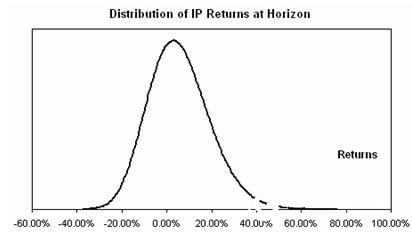
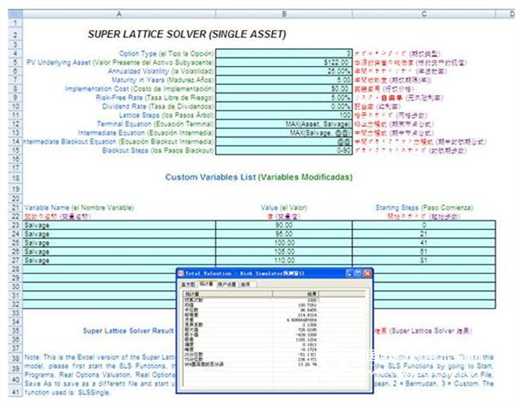
Risk Simulator Software Case: Risk-Based Management Compensation Assessment This article was provided by Real Options Valuation, Inc, published by China Science Software Network The case was written by Patrick Haggerty, head of an executive compensation consulting firm, James F. Reda Associates LLC. As an independent management and board advisor, the company helps companies design and execute executive compensation plans. The company is very professional in the use of the Financial Accounting Standards Board Announcement Article 123 (2004 revised version), which is a stock-based compensation payment (FAS 123(R)) and its associated interpretation for long-term incentive assessment. Working with Dr. Johnathan Mun and using his options valuation package, James F. Reda Associates LLC helps clients identify and understand the impact of alternative long-term incentive programs on compensation costs. The case is based on a real project, but considering the protection of patent information, we use a fictitious name called Boris Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (Boris). This case is about Boris's assessment of alternative long-term incentive (LTI) program design and the fair value of expenditures required to determine new financial accounting standards. The management and compensation committees can jointly evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the various available LTI solutions through the following steps. These steps include: In the end, Boris decided to implement restrictive stock incentives, and only when a certain shareholder return target is reached can the reward be obtained. Since the performance condition is the total shareholder's return, the option pricing model can be used to determine the fair value of the barrier option, in which the stock can only be granted if the predetermined limit is exceeded. Simple Black-Scholes are not used to price these options. In contrast, Monte Carlo and binary tree models, such as Dr. Mun's Real Options Super Lattice Solver and Risk Simulator® software, are most suitable because they contain the necessary input factors. US Financial Accounting Standards Bulletin No. 123 (FAS 123(R)) defines the conditions for granting Boris's restricted stock incentives as “market conditionsâ€, meaning that it is linked to stock prices. This feature is important because if the award criteria in the Boris plan design are not related to the stock price (for example, earnings per share or earnings per share, and no profit before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, or EBITDA), Performance conditions are included in the incentive fair value (FAS 123(R) makes this performance measure a “performance conditionâ€). background Boris Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a publicly traded $1 billion chemical manufacturer. The company has 2,000 employees, of which about 200 are management and administrative staff. Boris' compensation committee is responsible for determining executive compensation levels and LTI incentives for all employees. The Compensation Committee evaluated the compensation measures of peer companies and decided that LTI should be a significant and important part of total compensation. As a result, the company has implemented LTIs incentives for management and executives. Historically, Boris has implemented stock option incentives for employees because the cost was zero before FAS 123(R) - under previous accounting standards, if the number of shares is known on the authorization date, then the salary fee in the state of the parity option Zero. Boris' stock option incentives did not provide incentives to shareholders or contact shareholders as expected by the compensation committee. In the past four years, Boris's share price has been relatively unstable and has generally declined somewhat. About half of the stock options offered by Boris to employees are higher than the current price of the stock or are in a discounted state. Furthermore, the company continues to provide stock option incentives as its share price continues to fall. As a result, the company has more worthless stocks, and employees have very little contact with shareholders, and there are only a few stocks left in their stock pool. As will be discussed below, the Compensation Committee decided to conduct a study to evaluate these issues. Compensation committee process The Compensation Committee has taken the following steps to study the LTI design: 1. Review historical LTI incentives Purpose: To understand what types of rewards employees have in the past, what are the current fair value awards and what else they have. The result: In the past three years, Boris has awarded approximately 900,000 options per year (a total of 2.7 million for three years). Unfortunately, about half of the options are discounted, and only a few employees can exercise and sell the stock to earn income. 2. Check the company's long-term incentive plan Purpose: To understand the various LTI forms in the LTI program approved by the shareholders and how many shares can be used to reward. Result: Boris' LTI program is flexible and allows for any type of LTI form, including: Since the stock option grant has exceeded expectations in the past three years, the company will only have 500,000 shares available for future. It seems that Boris will need to turn to shareholders next year because they want to apply the remaining shares smarter. 3. Conducting market research Purpose: To identify competitive LTI incentives, costs, and LTI design measures (penalty retention, performance measurement, suspension clauses, and holding period). Results: According to the analysis of competitors in the industry, the company's previously determined stock option incentives are higher than the market level – based on individual positions, fund suspensions and costs. In addition, the company has determined that many peer companies offer full-value stocks (such as restricted stocks and performance stocks) rather than stock options. Among the peer companies that use performance as a condition for all-stock incentives, the most common performance conditions are total shareholder earnings, earnings per share, and EBITDA. 4. The strengths and weaknesses of each LTI incentive form were evaluated, and Table 1.1 summarizes these conclusions of the Compensation Committee. Compensation committee decision The Remuneration Committee decides to implement restrictive stock incentives and achieve the predetermined total shareholder return target. The main factors affecting the Remuneration Committee's selection of this LTI program include: Design details include: Types of Restricted stock Grant criteria Annual total shareholder income (TSR) reaches 6% Execution period Three years (average cumulative TSR must exceed 6%) Dividend rights Participants can only receive a dividend after granting the stock. Number of shares Zero-sum awards, no matter whether the TSR exceeds or falls below 6%, the number will not be adjusted. Before choosing 6% as the TSR target, the Compensation Committee studied Boris's historical TSR. According to the study, Boris' average annual rate of return for the past three years was 5.2%. Using this figure and volatility estimates, we can calculate the expected expected return distribution (see Figure 1.1). The Committee refers to these to set the expected range of TSR goals and TSR performance: TSR target 6% Minimum expectation 0% Most likely value 5% Maximum expectation 9% Figure 1.1 Expected revenue distribution The Compensation Committee considered and analyzed the following alternative program designs, but did not adopt them. Each alternative generates a different fair value calculation. Compensation committee regulations Using the FAS123(R) manual, the Boris Compensation Committee has determined the fair value of restricted stock to confirm the fee. The salary cost of the award is equal to the fair value multiplied by the number of shares granted. Under FAS123's forecast disclosure rules, the fair value determination process for restricted stocks and stock options is similar. However, the simple Blacks-Scholes model cannot be used to determine the fair value of rewards with TSR targets. Instead, Monte Carlo simulations and binary tree models must be used, the inputs of which will be detailed later. The combination of Monte Carlo simulation and the binomial model is more appropriate than other closed option pricing models because the analysis has a boundary associated with the clearing structure (that is, the TSR target), which means that only the binary tree can be used as a barrier option. Modeling. In addition, the possibility that Boris's TSR exceeds these targets is uncertain, then we need to perform a Monte Carlo simulation to get its expectations. Therefore, we use the Monte Carlo simulation function of Risk Simulator®, Employee Stock Option Valuation and Real Option SLS software for calculation. For more details on running SLS software, see the chapter on real option analysis, or refer to the author's Real Option Analysis, Second Edition (Wiley Finance, 2005). The following are the assumptions used in the model: dividend dividend Stock price Quarterly bonus Date of payment Quantity interest rate 3/15/2005 .04 $15.00 0.27% 6/15/2005 .04 $15.50 0.26% 9/15/2005 .04 $15.75 0.25% 12/15/2005 .04 $16.00 0.25% Total dividend income per quarter 1.03% The Monte Carlo simulation and Real Options SLS software used yielded a fair value of $10.27 (Figure 1.2). Real Options SLS software is used to obtain the fair market value of restricted stocks and Risk Simulator® software is used to simulate TSR possible values. Thus, if Boris rewards 400,000 restricted stocks, the pay cost is equal to 400000 × $10.27 = $4108000, which will increase during the three-year implementation period. If you do not use the Monte Carlo simulation model, Boris will be required to use the authorization date price of $20, and the result is 400000 × $20 = $8000000. Therefore, by applying the right approach and the right LTI design, Boris can cut costs by 50%. in conclusion By speculating the impact of specific changes on fair value, Monte Carlo simulations can be used to help design LTI incentive plans and determine the fair value of LTI awards under FAS 123R. If we do not use this complicated method, we will never calculate the fair value of the fight, nor will we make the decision to implement the correct LTI. In addition, the method described here can be used for many other purposes, such as with market indices (such as the S&P 500 index), company performance (for example, we can use financial data such as net profit margin, gross margin, EBITDA, and others). Or some commodity price-linked LTI design and stock-based compensation. For more details on the technology and applications of FAS 123R and Employee Stock Valuation software, see Valuing Employee Stock Options (Under 2004 FAS 123) (Wiley Finance, 2004). Figure 1.2 Monte Carlo simulation and SLS analysis For more information on Risk Simulator software, please visit the China Science Software Network. It help you create a gorgeous look, or split hair. Using this hair clip can make wavy hair for you, classical style, retro style, wedding dress style can also be used, bring you a classic style. Hair Clips,Metal Duckbill Clips,Metal Duckbill Hair Clips,Hair Styling Clips Xuchang Le Yi De Import And Export Trade Co., Ltd. , https://www.lileaderbeauty.com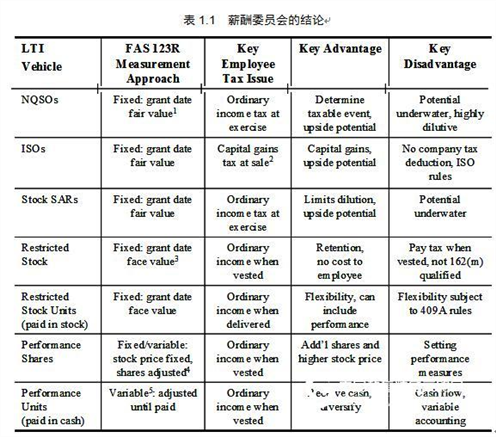
Each hair clip the lengthening design makes it easier to stabilize the hair style, making the hair clip firmer. the edge of clip is polished, smooth and not easy to hurt the scalp, the handle is anti-skid design, with high quality spring, tight bite and good fixity.
High quality metal manufacturing, hairpin front arc in line with the head design, can better fit the scalp, not easy to hurt the scalp. Hair clips can be flexible opening and closing, and firmly hold the hair without sliding.
Barber's professional assistance tools, making waves and curls of the hair clips. You can also separate parts of your hair during a haircut, hair coloring, or dry your hair. They are suitable for DIY enthusiasts to make butterfly hair clips and so on.